![]() The Project funded by The National Science Centre, Poland, in the framework of the program “SONATA BIS 4”.
The Project funded by The National Science Centre, Poland, in the framework of the program “SONATA BIS 4”.
| PL |
The manuscripts from the Mardzong Caves in Mustang,
Nepal: interpretation, paper analysis and dating
This project aims to study, date, and preserve the collection of Tibetan manuscripts discovered in Mardzong. The Mardzong manuscripts are exceptional, like the more archaic caches of Silk Road manuscripts from Central Asia, but they are not yet known. Through our research, dating, cataloguing, and photographing, we aim to make these manuscripts available to Western scholars, the Tibetan community, and people in Nepal. Overall, our aim is to build, via scientific analysis of the paper on which the texts are written as well as codicological study, a solid geographical and periodical catalogue that will cover at least the last two centuries, and provide data for earlier works found in caves as well. By expanding the scope of research from the manuscripts’ textual content to their material characteristics, we move beyond legends to a more precise understanding of the history of the Mardzong deposit and its role in the local community in the past.
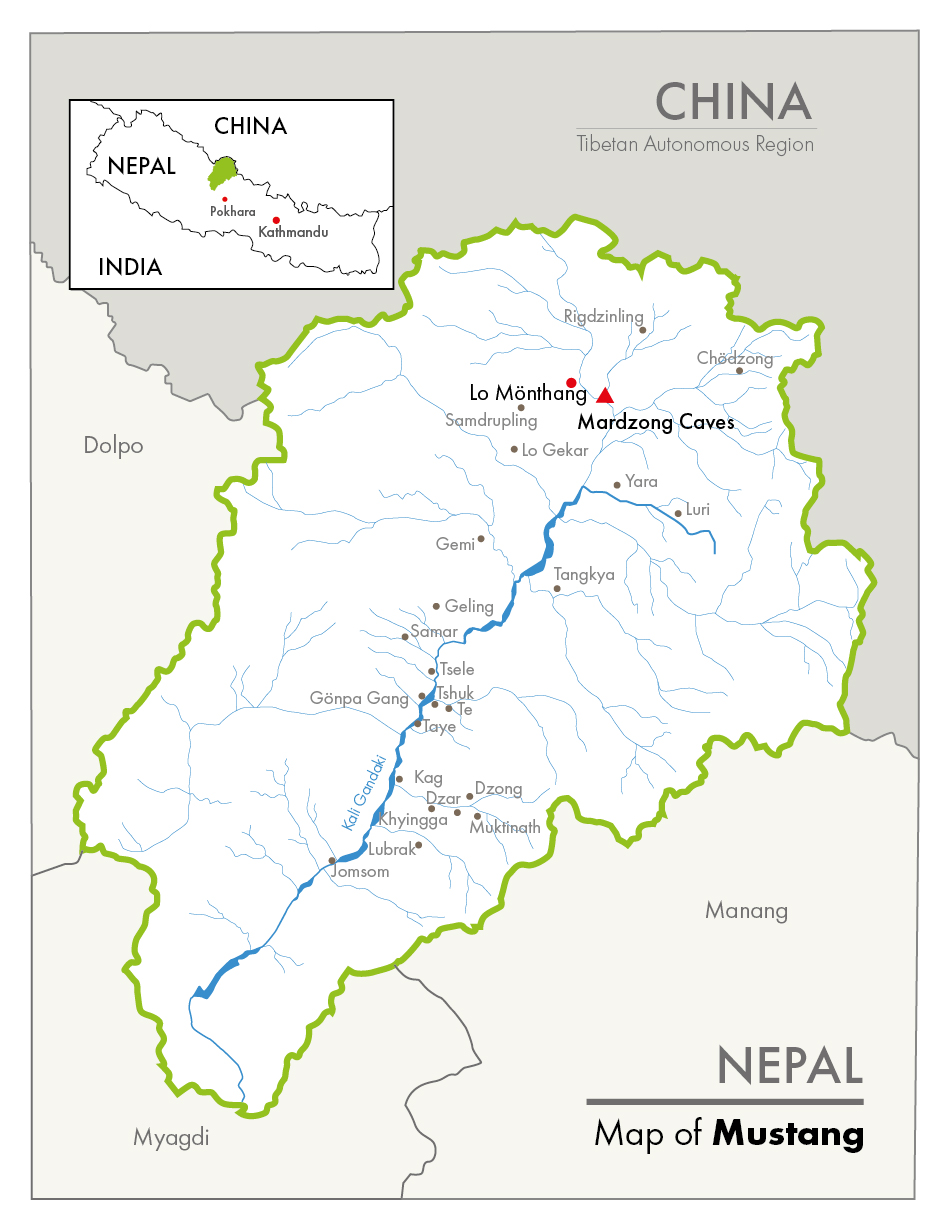
Mardzong manuscripts discovery
The Mardzong manuscripts are an extraordinary archaeological find. They comprise an information-dense repository of artifacts, history, and ideas spanning half a millennium. The collection was discovered in 2008 by a group of climbers led by Brot Coburn and Peter Athans in a cave complex called Mardzong, south of Lo Monthang, in Nepal’s Mustang District (the expedition is documented in the National Geographic Film Secrets of Shangri-La).
The Mardzong caves appear to have been used as a cache for various libraries, apparently from settlements around Lo Monthang that were abandoned. Within the same cave complex archaeologist Mark Aldenderfer, University of California, Merced, discovered several 6th-century burial sites containing human skeletons and artifacts made of wood, textile, metal, and other materials (documented in the National Geographic Film Sky Caves of Nepal; further discoveries were documented in the PBS Nova Film Secret of the Sky Tombs). The team also found 13th-century Tibetan Buddhist shrines decorated with exquisitely painted murals, including a 55-panel depiction of Buddhist saints (documented in Buddhist Lost Cave Temples).